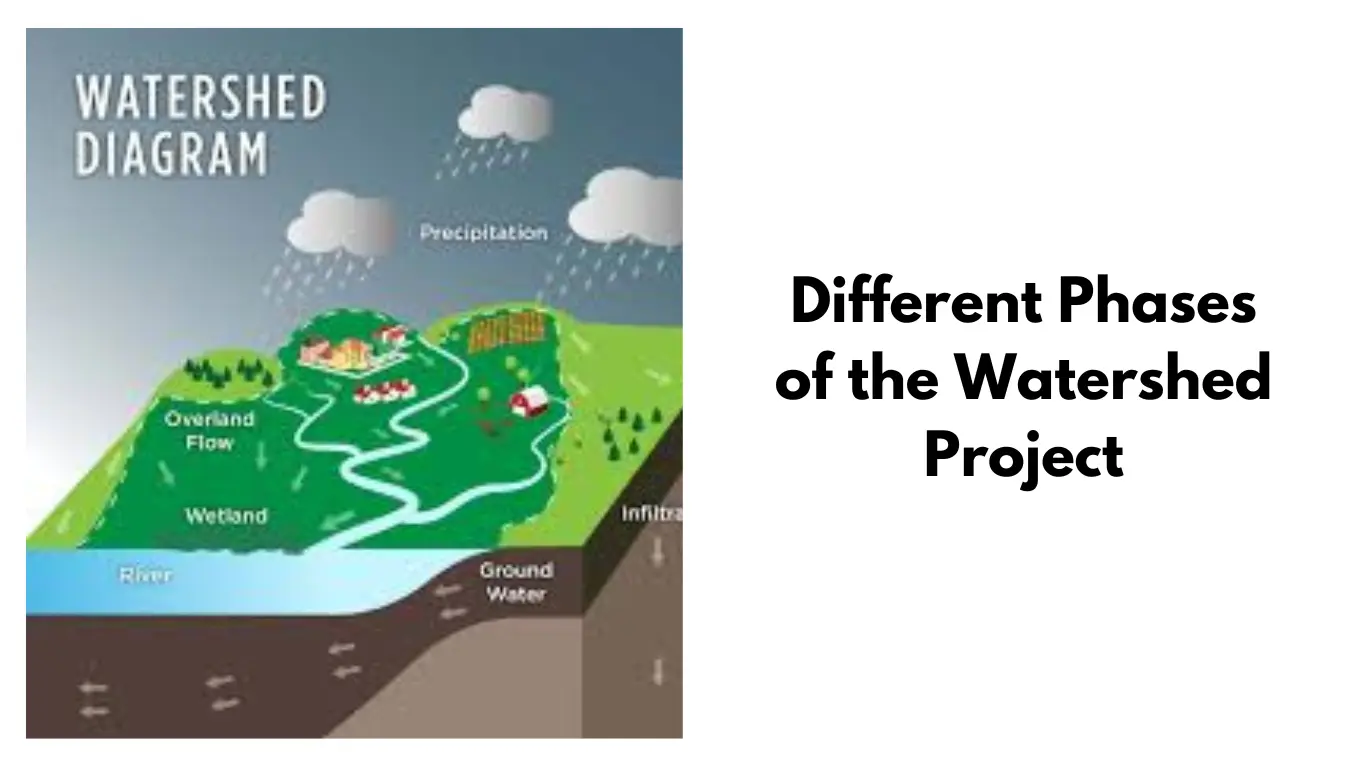
Hey! Watershed projects are crucial in conserving natural resources, enhancing agricultural productivity, and improving rural livelihoods. This project’s main focus is managing water and soil resources sustainably within a defined geographical area.
Phases of a Watershed Project
Following are the phases of the watershed project.
1. Pre-Planning Phase:
Community Engagement: The first step is to engage local communities. here raising awareness about the project’s goals and encouraging active participation is carried out.
Baseline Data Collection: collecting information about the area’s topography, soil quality, rainfall patterns, and socioeconomic conditions is done here. This helps in designing a relevant and effective plan.
2. Planning Phase
As groundwork is completed, detailed planning starts.
Preparing a Watershed Development Plan: Experts develop a plan for soil conservation, water harvesting, and livelihood improvement.
Setting Goals and Priorities: Here Measurable objectives are defined, and priorities are set based on environmental conditions.
Year-Wise Activities in the Implementation Phase
The implementation phase is where the action begins.
- Year 1: Awareness Campaigns and Capacity Building.
- Year 2: Soil and Water Conservation Measures.
- Year 3: Vegetative Cover Enhancement.
- Year 4: Infrastructure Development and Monitoring.
- Year 5: Consolidation and Sustainability.
Year 1: Awareness Campaigns and Capacity Building.
firstly Educating the community about sustainable practices, the importance of water conservation, and the project’s benefits. after that Providing training sessions for farmers to equip them with the skills needed for soil and water conservation techniques.
Year 2: Soil and Water Conservation Measures.
Activities like contour bunding, terracing, and gully plugging are invented to reduce soil erosion and improve its fertility. Building check dams, percolation tanks, and farm ponds to enhance water availability and recharge groundwater.
Year 3: Vegetative Cover Enhancement.
here we are planting trees and shrubs to increase green cover and stabilize the soil Grassland development is carried out by Encouraging the growth of native grasses to prevent soil erosion and improve grazing conditions.
Year 4: Infrastructure Development and Monitoring.
In Infrastructure Development Construction of rural roads, storage facilities, and market linkages to improve accessibility and support economic activities and in monitoring Regular assessments to evaluate the project’s progress is carried out.
Year 5: Consolidation and Sustainability.
Consolidation ensures that the community is equipped to maintain the structures. Sustainable Practices Establishes community-led institutions and frameworks to continue conservation efforts independently.
Importance of Year-Wise Activities:
- Reduced soil erosion and improved fertility.
- Enhanced water availability.
- Higher agricultural productivity.
- Increased biodiversity due to afforestation.
- Better livelihood opportunities for rural communities.
More Questions: